IT and Cybersecurity Cheat Sheets
As much as we try to be proactive about cybersecurity, IT planning, or project management, we get distracted, or procrastinate. These cheat sheets, checklists and templates are designed to assist professionals in difficult situations, even if they find themselves unprepared.
Writing Tips for IT Professionals
Technical writing requires understanding your readers’ expectations and keeping messages as short and simple as possible to achieve objectives. Key practices include deleting unnecessary words, avoiding passive voice, leading with important points, and seeking feedback on structure, look, words, and content.
Tips for Creating and Managing New IT Products
Product managers determine what to build, align roadmaps to business strategy, and drive product adoption by working with customers, sales, and engineering teams. Success requires understanding market segmentation, defining a minimum viable product, establishing the right pricing model, and accounting for operational needs during delivery.
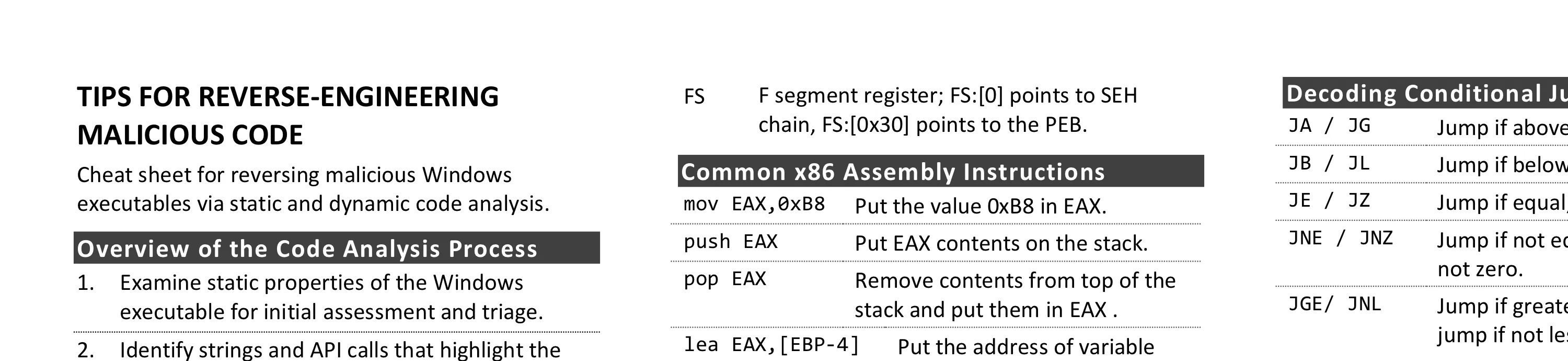
Tips for Reverse-Engineering Malicious Code
Reversing malicious Windows executables involves examining static properties, identifying suspicious strings and API calls, performing behavioral analysis, and using disassemblers and debuggers. Key areas include understanding x86/x64 registers, common assembly instructions, risky API calls for code injection, DLL loading, and keylogging.
Tips for Getting the Right IT Job
Landing the right IT job requires advance preparation, strategic networking, and treating interviews as two-way conversations. Key practices include understanding the role’s requirements, customizing your resume, researching interviewers, and negotiating compensation packages with awareness of your alternatives.
REMnux Usage Tips for Malware Analysis on Linux
REMnux provides a curated Linux environment for malware analysis, with tools organized by task: Windows PE analysis, Linux binaries, documents, network interactions, memory forensics, and data gathering. Docker containers extend capabilities for tools like Thug honeyclient, RetDec decompiler, and Radare2.
Tips for Creating a Strong Cybersecurity Assessment Report
Creating a strong security assessment report requires analyzing data beyond tool output, prioritizing findings by risk, documenting methodology and scope, and providing practical remediation guidance. Key qualities include a strong executive summary, logical structure, and concrete statements that avoid passive voice.
Critical Log Review Checklist for Security Incidents
Log review for incident response and routine monitoring involves copying logs centrally, minimizing noise by removing benign entries, verifying timestamps, focusing on changes and failures, working backwards in time, and correlating across sources. Key entries to find span Linux, Windows, network devices, and web servers.
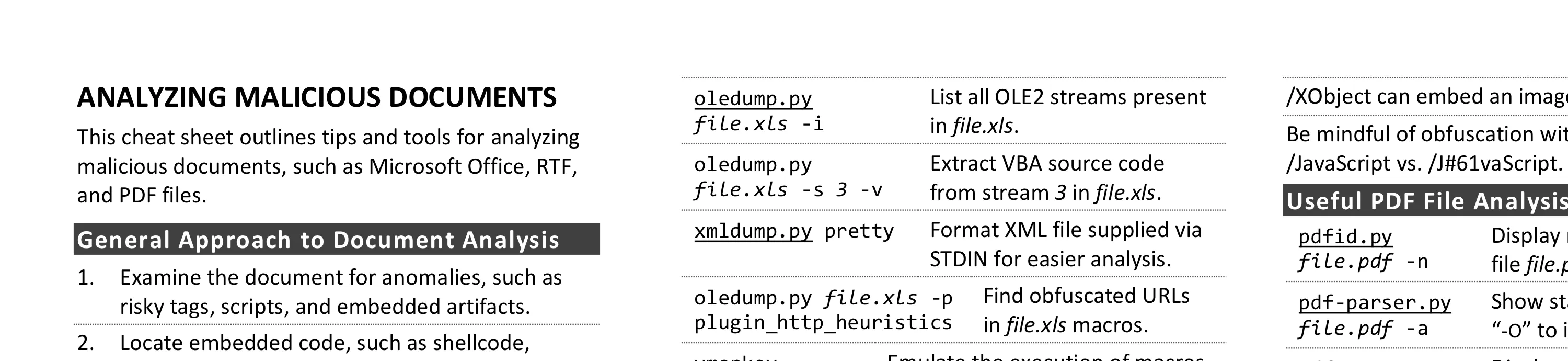
Cheat Sheet for Analyzing Malicious Documents
Analyzing malicious documents involves examining files for anomalies, locating embedded code like macros or JavaScript, extracting and deobfuscating suspicious content, and emulating shellcode. Key tools include olevba for Office macros, pdfid for risky PDF keywords, and xlmdeobfuscator for Excel 4.0 macros.
Security Architecture Cheat Sheet for Internet Applications
Initial design and review of Internet application security architecture covers four areas: business requirements (data classification, users, partners, regulations), infrastructure requirements (network, systems, monitoring), application requirements (data processing, access, monitoring), and security program requirements (operations, change management).
Troubleshooting Human Communications
Effective communication requires empathy, acknowledging different perspectives, and phrasing arguments using the other person’s terminology and objectives. Key tips cover email best practices, in-person conversations, presenting to executives, and improving skills through improv classes or Toastmasters.
Security Incident Survey Cheat Sheet for Server Administrators
Server administrators examining suspect systems should avoid actions that access many files; instead look at logs, network connections, users, processes, scheduled jobs, and auto-start programs. Specific commands for Windows and Unix systems help decide whether to escalate for formal incident response.
Initial Security Incident Questionnaire for Responders
Incident handlers assessing situations should ask the right questions: understanding background (how detected, security posture), defining communication parameters (coordinator, decision-makers, encryption), assessing scope (affected systems, compliance obligations), reviewing initial survey results, and preparing for next steps.
Network DDoS Incident Response Cheat Sheet
DDoS response requires preparation before attacks occur: establish ISP contacts, create allowlists of critical source IPs, lower DNS TTLs, and document infrastructure. During attacks, analyze traffic patterns to differentiate malicious from legitimate traffic, and throttle DDoS traffic as close to the network edge as possible.
Malware Analysis and Reverse-Engineering Cheat Sheet
Malware analysis combines behavioral examination with static and dynamic code analysis to understand malicious software. Key steps include using automated sandboxes for triage, monitoring system and network interactions, examining code with Ghidra and x64dbg, and unpacking protected specimens.
Information Security Assessment RFP Cheat Sheet
Effective security assessment RFPs require understanding what’s driving the need, ensuring staff availability, and defining realistic timelines and budgets. Key elements include specifying assessment objectives, expected deliverables, and criteria for vendor selection based on staff expertise and project management capabilities.
How to Suck at Information Security
A tongue-in-cheek collection of common security mistakes to avoid: deploying products without tuning them, treating all assets with equal rigor regardless of risk, locking down infrastructure so tightly that work becomes difficult, and assuming compliance equals security.
Report Template for Threat Intelligence and Incident Response
Large-scale intrusions require organizing intelligence about adversary actions and response efforts. A threat intelligence report template leveraging the Intrusion Kill Chain, Courses of Action Matrix, and Diamond Model helps capture key details about adversary tactics, victim characteristics, and defensive actions in a comprehensive manner.