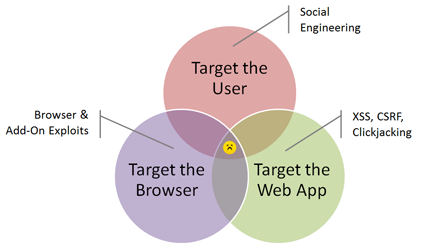
Three Web Attack Vectors Using the Browser
Three browser attack vectors cause most web-based attacks: social engineering (phishing, fake software installs), attacking web applications through the browser (XSS, CSRF, clickjacking), and exploiting client-side vulnerabilities in browsers and plugins like Flash, Reader, and Java. Most attacks combine one or two of these.
Three web attack vectors seem to be responsible for the majority of computer attacks that involve a web browser:
- The attack can incorporate an element of social engineering to persuade the victim to take an action that compromises security. For instance, the victim can supply data to a phishing site or install a program that will turn out to be malicious.
- The attacker can use the browser as a gateway for attacking web applications via techniques such as cross-site scripting (XSS), Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and Clickjacking.
- The attacker can exploit a vulnerability in the web browser or in local software that the browser can invoke. Such client-side exploits have targeted browser add-ons such as Flash, Adobe Reader and Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
Most attacks include one or two of the three techniques. For instance, Koobface worm targets the user (social engineering to click links) and the web application (hijacking social networking site sessions). An attack that combines all elements would be particularly effective (do you know of any examples?).
The following series of posts explores these three web browser attack vectors in greater detail, discussing how enterprises can protect themselves against such attacks: