Memory forensics is becoming an essential aspect of digital forensics and incident response. When a system is believed to have been compromised or infected, the investigator needs a convenient way to take a memory snapshot of the host. DumpIt, a convenient tool from Comae Technologies, makes this very easy, even if the person in front of the affected computer isn't technical. This tool is a part of the free Comae Memory Toolkit. (An earlier version of this tool was distributed by MoonSols, which no longer makes it available.)
DumpIt is a fusion of two trusted tools, win32dd and win64dd, combined into one one executable. provided to a non-technical user using a removable USB drive. The person needs to simply double-click the DumpIt executable and allow the tool to run. DumpIt will then take the snapshot of the host’s physical memory and save it to the folder where the DumpIt executable was located.
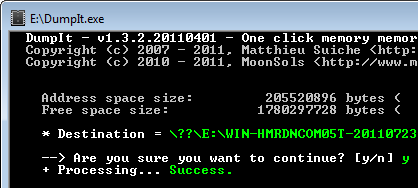
The user can then provide the investigator with the USB key, which will contain the memory snapshot file. The administrator can use free memory forensics tools such as The Volatility Framework, Rekall or Redline to examine the memory file's contents for malicious artifacts.
DumpIt provides a convenient way of obtaining a memory image of a Windows system even if the investigator is not physically sitting in front of the target computer. It's so easy to use, even a naive user can do it. It's not appropriate for all scenarios, but it will definitely make memory acquisition easier in many situations.